前言
最近因為工作需要,要透過JSON-C這個library對JSON格式的資料進行處理。
這邊筆記一下相關的使用方法。
環境與安裝
本來打算clone source code下來之後自己build,不過過程遇到一些問題,以後有時間解決再更新上來。
我的操作環境是Ubuntu Bionic (18.04LTS),可以直接用apt-get取得:
1
| sudo apt-get install libjson-c-dev
|
不過僅能取得版本0.12.1的JSON-C,而JSON-C有一個可以走訪整個JSON Object的實做(json_visit)要再0.13版才有,暫時玩不到了,以後有機會再補。
安裝完之後可以確認一下header檔與library的位置:
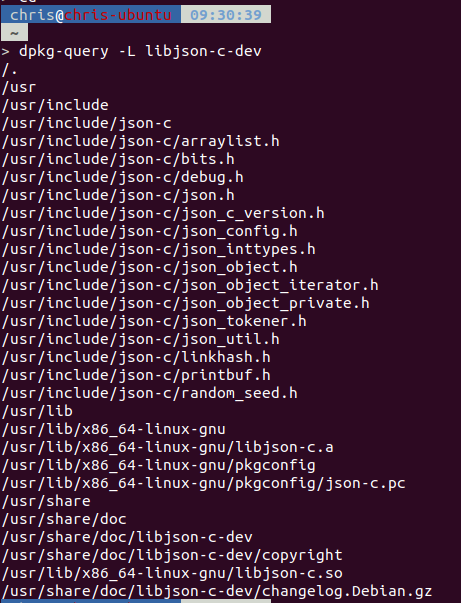
使用方式
初始化JSON Object
因為懶得每次都要打很長一串的struct type,先做一個typedef,接著使用json_object_new_object()初始化一個空的JSON Object作為根物件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <json-c/json.h>
typedef struct json_object* jsonObj;
int main(){
jsonObj root = json_object_new_object();
return 0;
}
|
建立與加入物件
接著可以透過json_object_new_string()、json_object_new_int()等…函數來建立JSON Object。
支援的型態包括:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| json_type_null
json_type_boolean
json_type_double
json_type_int
json_type_string
json_type_object
json_type_array
|
實際用法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| jsonObj obj = json_object_new_string("Chris");
json_object_object_add(root, "name", obj);
obj = json_object_new_int(30);
json_object_object_add(root, "age", obj);
jsonObj arrObj = json_object_new_array();
obj = json_object_new_int(1);
json_object_array_add(arrObj, obj);
obj = json_object_new_int(2);
json_object_array_add(arrObj, obj);
json_object_object_add(root, "array", arrObj);
|
JSON Parser
另外也可以在JSON Object中加入其他的Object,來源可以是透過將JSON字串內容pase成JSON Object,或者是透過讀取JSON檔案。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| obj = json_tokener_parse("{'address':'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX', 'deposit':999999999, 'arr':[3, 4, 5]}");
json_object_object_add(root, "info", obj);
|
物件的走訪
這邊實做一個function,除了印出基本型態的物件內容外,也可以用遞迴的方式將物件內包含的其他物件進行走訪。
之後有機會嘗試json_visit的話再補上。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| void visit(jsonObj root){
static int level = 0;
struct json_object_iterator it;
struct json_object_iterator itEnd;
it = json_object_iter_begin(root);
itEnd = json_object_iter_end(root);
while (!json_object_iter_equal(&it, &itEnd)) {
printf("\r\n");
for(int i=0; i<level; i++) printf("\t");
printf("%s ",json_object_iter_peek_name(&it));
jsonObj obj = json_object_iter_peek_value(&it);
struct array_list * list = NULL;
switch(json_object_get_type(obj)){
case json_type_boolean:
printf("%d", json_object_get_boolean(obj));
break;
case json_type_double:
printf("%f", json_object_get_double(obj));
break;
case json_type_int:
printf("%d", json_object_get_int(obj));
break;
case json_type_string:
printf("%s", json_object_get_string(obj));
break;
case json_type_array:
list = json_object_get_array(obj);
for(int i=0; i<list->length; i++){
printf("%d ", json_object_get_int(json_object_array_get_idx(obj, i)));
}
break;
case json_type_object:
level++;
visit(json_object_get(obj));
break;
case json_type_null:
default:
break;
}
json_object_iter_next(&it);
}
level--;
printf("\r\n");
}
|
完整程式碼
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <json-c/json.h>
typedef struct json_object* jsonObj;
void visit(jsonObj root){
static int level = 0;
struct json_object_iterator it;
struct json_object_iterator itEnd;
it = json_object_iter_begin(root);
itEnd = json_object_iter_end(root);
while (!json_object_iter_equal(&it, &itEnd)) {
printf("\r\n");
for(int i=0; i<level; i++) printf("\t");
printf("%s ",json_object_iter_peek_name(&it));
jsonObj obj = json_object_iter_peek_value(&it);
struct array_list * list = NULL;
switch(json_object_get_type(obj)){
case json_type_boolean:
printf("%d", json_object_get_boolean(obj));
break;
case json_type_double:
printf("%f", json_object_get_double(obj));
break;
case json_type_int:
printf("%d", json_object_get_int(obj));
break;
case json_type_string:
printf("%s", json_object_get_string(obj));
break;
case json_type_array:
list = json_object_get_array(obj);
for(int i=0; i<list->length; i++){
printf("%d ", json_object_get_int(json_object_array_get_idx(obj, i)));
}
break;
case json_type_object:
level++;
visit(json_object_get(obj));
break;
case json_type_null:
default:
break;
}
json_object_iter_next(&it);
}
level--;
printf("\r\n");
}
int main(){
jsonObj root = json_object_new_object();
jsonObj obj = json_object_new_string("Chris");
json_object_object_add(root, "name", obj);
obj = json_object_new_int(30);
json_object_object_add(root, "age", obj);
jsonObj arrObj = json_object_new_array();
obj = json_object_new_int(1);
json_object_array_add(arrObj, obj);
obj = json_object_new_int(2);
json_object_array_add(arrObj, obj);
json_object_object_add(root, "array", arrObj);
obj = json_tokener_parse("{'address':'XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX', 'deposit':999999999, 'arr':[3, 4, 5]}");
json_object_object_add(root, "info", obj);
visit(root);
return 0;
}
|
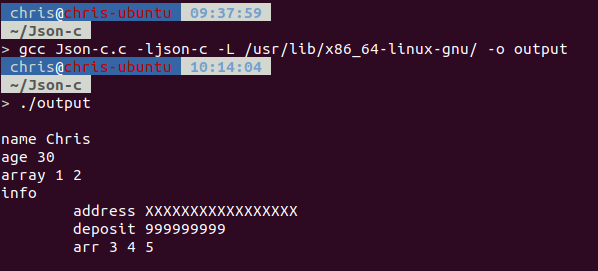
編譯與執行
透過gcc進行編譯,指定json-c library的搜尋目錄與link名稱。
1
| gcc Json-c.c -ljson-c -L /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ -o output
|
參考連結
官方文件

